As promising carbon dioxide (CO2) adsorbents, metallic-organic and natural frameworks (MOFs) have captivated considerably notice in the subject of carbon seize and storage (CCS).
In addition to the adsorption home, the electrical power overall performance similar to the regeneration procedure is also a very important element when screening for suitable MOF adsorbents.
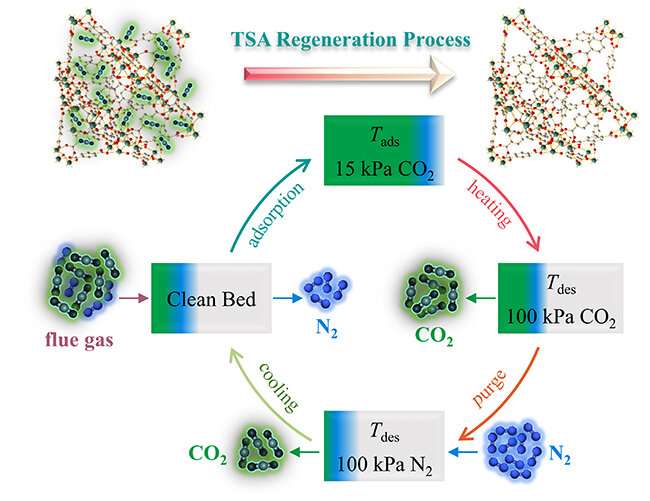
Recently, a investigate group led by Prof. Shi Quan from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in collaboration with Prof. Han Wei from the Hong Kong University of Science and Technological know-how, proposed an experimental strategy to investigate the energy general performance of MOF adsorbents for CO2 seize in the temperature swing adsorption (TSA) system.
This examine was revealed in the Chemical Engineering Journal on April 10.
The approach is based on the blend of calorimetry and thermal evaluation process. The researchers evaluated 5 effectively-characterised isomorphic zirconium-based MOFs working with this technique.
They analyzed the CO2 adsorption and desorption procedure making use of a thermogravimetric evaluation instrument with a temperature-move application, and established the desorption temperatures for these MOFs. The CO2 uptake and desorption heats of these MOFs ended up obtained from general isothermal adsorption measurements.
A lot more importantly, the certain heat capacities of these MOFs had been measured utilizing a rest calorimeter, and their practical warmth values in the temperature swing assortment had been calculated appropriately.
“The strength qualities involved in the TSA course of action, such as the regeneration vitality, CO2 operating ability, and the corresponding parasitic power, ended up efficiently and reliably evaluated,” reported Prof. Shi.
The benefits indicated that the sensible warmth for heating the adsorbents from adsorption temperature to desorption temperature dominated the regeneration strength, and the parasitic energy was inversely proportional to the working capability.
The proposed strategy consists of several assumptions, and has ample resolution to distinguish modest discrepancies in power performance-similar properties of MOFs with identical buildings and/or compositions.
“This new technique could present a feasible and effective experimental approach to examine and assess the opportunity of adsorbents for CO2 seize,” mentioned Prof. Shi.
“This get the job done can be a superior reference for MOF adsorbent testing metrology growth,” commented one particular of the reviewers.
Scientists suggest new approach for electrocatalytic hydrogenation of acetylene to ethylene less than area temperature
Ji-Peng Luo et al, An experimental method for evaluating the electricity overall performance of metal–organic framework-dependent carbon dioxide adsorbents, Chemical Engineering Journal (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.136210
Citation:
Method for analyzing power overall performance of metal-natural-framework-centered carbon dioxide adsorbents (2022, April 14)
retrieved 16 April 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-04-system-electrical power-metallic-organic-framework-based mostly-carbon-dioxide.html
This document is subject matter to copyright. Aside from any good dealing for the function of personal research or study, no
part could be reproduced without the need of the written authorization. The content material is offered for information and facts functions only.






