Open up source software’s share of the typical codebase grew to 78% in 2021, but corporations ongoing to use components that are out of day and no extended managed, leaving their program probably vulnerable, a new analyze exhibits.
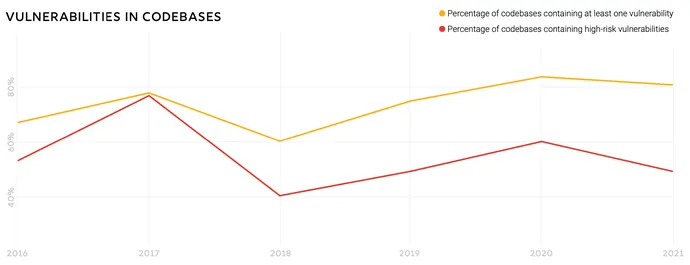
The extensive greater part of program codebases incorporate at least one vulnerability (81%), use an open up source element that is more than 4 several years out of date (85%), and comprise factors that have had no progress in the past two many years (88%), in accordance to Synopsys’ annual “Open Source Program Danger Evaluation” (OSSRA) report, posted this 7 days. Nonetheless, many of the facts points present enhancement more than very last calendar year, when 84% of codebases had at least a single vulnerability and 91% had no development action in the preceding two a long time.
General, the info suggests that providers are just commencing to make headway in opposition to vulnerabilities and there is nevertheless a long way to go, states Tim Mackey, principal security strategist at Synopsys.
“This complete of strategy [of] folks hoping to get their act alongside one another all-around what they would do from a software program offer chain standpoint is resonating to some extent, but it is not nevertheless at a point wherever it is building a major dent in big factors,” he says. With numerous of these open source components, “individuals are not expressing, I’m heading to use [component X,] it is coming alongside for the trip with some other library that they are making use of.”
The Synopsys report is a exceptional search into the point out of software package protection and license compliance, as the knowledge comes exclusively from the company’s provider for due diligence that commonly can take position for the duration of mergers and acquisitions (M&A). In 2021, the amount of M&As surged 24% thanks to rigorous opposition among company acquirers, non-public fairness firms, and unique-objective acquisition organizations (SPACs), in accordance to consulting company PricewaterhouseCoopers. The elevated action led to a surge in scanning codebases. Synopsys scanned more than 2,400 industrial codebases throughout 17 industries, a expansion of 64%, in accordance to the report.
Total, the enterprise observed improvements in lowering the number of superior-risk vulnerabilities in audited codebases, with a considerable lessen in the prevalence of best-10 high-danger vulnerabilities, the report mentioned. In the 2020 facts, for case in point, 29% of codebases experienced elements exposing the most commonplace vulnerability, though the 2021 knowledge in this year’s report discovered the most common large-possibility vulnerability in only 8% of codebases.
“All reoccurring significant-hazard vulnerabilities observed significant decreases,” the report states. “Prompt identification, prioritization, and mitigation of higher-hazard vulnerabilities can assistance teams handle the dangers that pose the best danger to their businesses.”
Open Source’s Persistent Unfold
The advancements occur as businesses proceed to deepen their use of open supply program. In 2019, open resource accounted for 70% of the codebases audited by Synopsys, climbing to 75% previous yr. Now at 78%, the protection of a firm’s application overwhelmingly relies upon on the point out of the open up supply parts applied by their improvement teams.
However the excellent of open supply program initiatives continues to be uneven, in particular when it arrives to safety. For illustration, nearly a quarter of computer software tasks (23%) have only a one developer contributing the bulk of the code, likely posing a threat to businesses that use the library as a ingredient of their individual program, in accordance to the report.
Sadly, businesses have not eliminated the most major pitfalls from open supply components and dependencies. With 88% of codebases containing outdated variations — components for which there is an update that has however to be applied — businesses will need to track the computer software and initiatives that they use in improvement with a software package monthly bill of elements (SBOM).
Far more SBOMs on the Way?
In the following 12 months or two, SBOMs will grow to be a great deal far more widespread, but that still will not address the concern, claims Mackey.
“The more substantial dilemma is that most individuals never know what to do with [the SBOM],” he claims. “It is an additional doc that sits along with the license settlement that no one reads, and they don’t know what to do about it, but they have read that it has some magic voodoo connected with it, so they want it, but they haven’t designed a procedure for working with it.”
As companies turn out to be far better about analyzing the elements utilised by their program, they will also obtain and repair a ton of licensing challenges as properly. Since all kinds of open up resource licenses exist, enterprises have to have to take treatment concerning what application they involve in their own progress. At this time, a lot more than half of audited codebases (53%) have license conflicts, and 20% include open up supply with no license or a nonstandard license.
In accordance to the Synopsys report, “Codebases that consist of open resource components with no discernible license or a personalized license have an further layer of risk.”
